Working with surface-mount devices (SMDs) requires precision, consistency, and the right combination of tools. Whether you are repairing smartphones, assembling printed circuit boards, or performing detailed electronics work, proper equipment is essential to achieve reliable solder joints. This guide provides a complete overview of the SMD soldering tools you need, how to choose them, and best-practice techniques to ensure professional results.

SMD Soldering Tweezer BA-7sa-14
Surface-mount soldering differs distinctly from traditional through-hole soldering. SMD components are smaller, lighter, and mounted directly onto PCB pads without leads passing through holes. Their compact size and tight spacing leave little room for error. Excessive heat can damage pads and traces, while insufficient heat produces weak joints. This is why specialized and more precise equipment is necessary for surface-mount work.
A high-quality soldering station with adjustable temperature control is the foundation of SMD soldering. Stable temperature output ensures consistent melting of solder without overheating sensitive components. Stations with digital displays and microprocessor control are ideal for maintaining thermal accuracy.
Many SMD components cannot be soldered or removed effectively with a soldering iron alone. A hot air rework station provides even heat distribution, allowing components such as QFPs, SOICs, and chip resistors to be reflowed or lifted safely. Adjustable airflow is important to avoid blowing away nearby components.
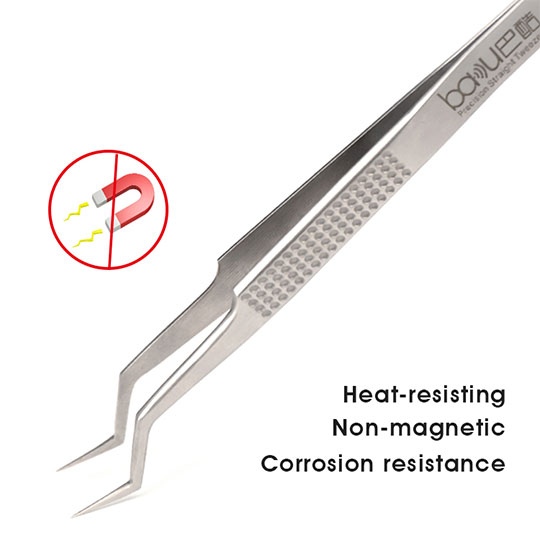
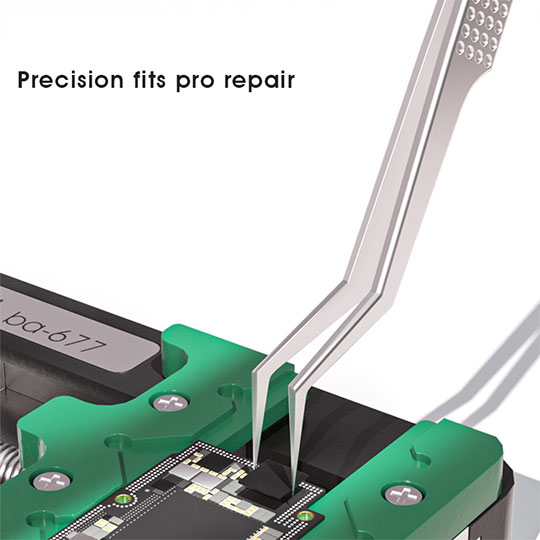
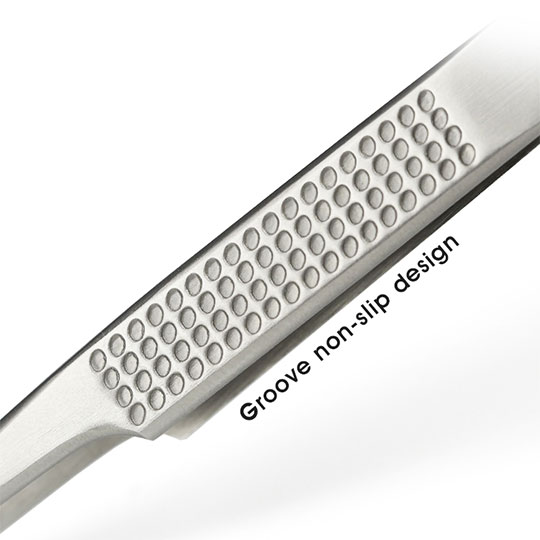
Fine-tip tweezers are essential for picking, placing, and adjusting tiny SMD components. High-quality stainless steel tweezers with non-magnetic and corrosion-resistant properties improve handling accuracy. Tweezers designed for SMD work should have a firm grip, an anti-slip texture, and pointed tips suitable for extremely small parts.
Flux improves solder flow and helps prevent oxidation, while solder paste is often used for reflow soldering or when working with stencils. High-purity isopropyl alcohol and cleaning brushes help remove residues and maintain a clean soldering environment, which is critical for consistent results.
De-soldering wicks, suction tools, and rework tools are needed for removal and correction work. Because SMD components are extremely small, magnifiers or microscopes should also be part of your setup. They help detect solder bridges, verify alignment, and ensure that joints are clean and reliable.
Equipment should maintain accurate temperatures during continuous operation. A good soldering station avoids temperature drops that lead to inconsistent joints. For hot air stations, both temperature and airflow control must be finely adjustable.
Different SMD components require different tip shapes or airflow patterns. A versatile soldering setup includes interchangeable soldering tips and multiple hot-air nozzles, helping you adapt to different projects and component sizes.
Comfortable grips, heat-resistant handle materials, and anti-static (ESD-safe) construction help ensure safety and accuracy. Quality tweezers, for example, should have a balanced feel and precise clamping force.

Reliable equipment brands provide spare parts, replacement tips, documentation, and customer support. Choosing reputable manufacturers ensures long-term stability for workshops and repair centers.
Beginners may start with a basic soldering station and a pair of precision tweezers, while professionals often need more advanced dual-function rework stations with digital controls. Select tools based on the complexity and frequency of your work.
Before soldering, clean PCB pads with isopropyl alcohol to remove oxidation and dirt. This ensures proper wetting and strong solder joints. Inspect the area with magnification to identify any potential issues.
For soldering irons, apply flux, heat the pad, and add solder carefully to avoid excessive buildup. For hot air soldering, preheat the area, apply uniform airflow, and wait for the solder to reflow. Avoid moving the component until the solder cools naturally.
After soldering, inspect joints for cold spots, bridging, or insufficient solder. Use magnifying tools to ensure each joint is well-formed. If corrections are needed, de-soldering tools can help remove excess solder or reposition components.
Regular cleaning of soldering tips, proper storage of tweezers, and keeping hot-air nozzles free from debris help extend the lifespan of your tools. Calibrate your soldering station regularly for optimal performance.
Good ventilation is essential when soldering to reduce exposure to fumes. Use ESD-safe mats and wrist straps to protect sensitive electronics. Besides, secure the PCB to prevent movement during soldering.

SMD soldering demands a combination of skill and high-quality equipment. With the right soldering station, hot air rework tools, accurate tweezers, and reliable flux and cleaning materials, you can achieve professional-grade results consistently. By following best practices and maintaining your tools, even challenging SMD projects become manageable and efficient. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional technician, investing in proper equipment ensures better performance, cleaner solder joints, and long-term reliability in all your electronics work.